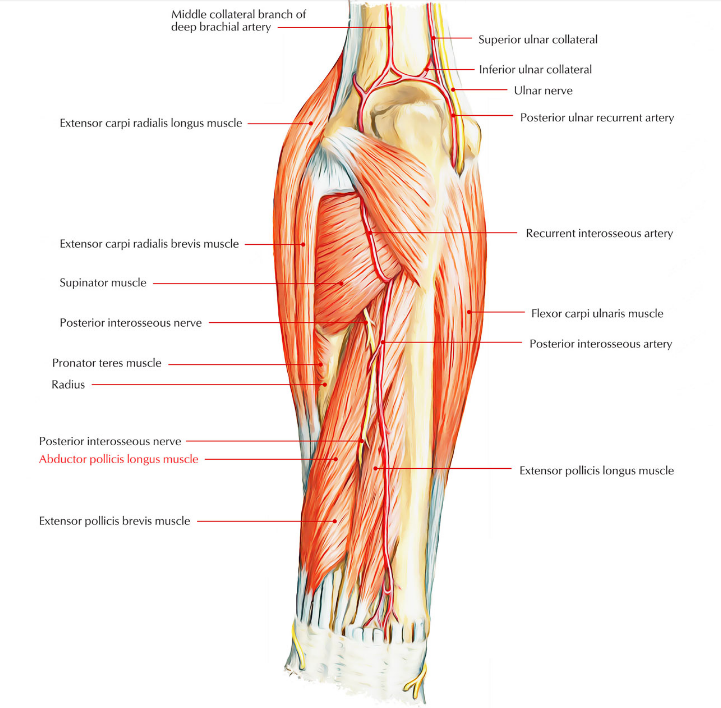
The abductor pollicis brevis is a key muscle in the human hand, playing a vital role in the movement and function of the thumb. Often overlooked in discussions of hand anatomy, this muscle contributes significantly to actions like gripping, pinching, and even fine motor tasks. Whether you’re a healthcare professional, a student of anatomy, or someone experiencing hand discomfort, understanding the abductor pollicis brevis is crucial.
In this article, we’ll explore the abductor pollicis brevis anatomy, its essential functions, clinical importance, and how conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome can affect it. By the end, you’ll have a thorough understanding of why this muscle matters in both health and clinical settings.
The Anatomy of the Abductor Pollicis Brevis
The abductor pollicis brevis is located in the thenar eminence, a group of muscles at the base of the thumb. This muscle originates from the flexor retinaculum and scaphoid bone and inserts into the proximal phalanx of the thumb.
Anatomically, the abductor pollicis brevis is one of the three muscles that make up the thenar muscles, which are responsible for thumb movement. These muscles work together to allow the thumb to perform its wide range of motions, which include opposition, flexion, and extension.
The muscle’s origin at the flexor retinaculum helps anchor it firmly within the hand, while its insertion on the thumb’s proximal phalanx enables the muscle to initiate abduction. This action is crucial for movements that involve spreading the thumb away from the hand, which is essential for functions like gripping and grasping objects.
One unique feature of the abductor pollicis brevis is that it is innervated by the median nerve, which is why it can be affected in conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome. Understanding its precise anatomical positioning is essential for diagnosing injuries or disorders affecting hand mobility.
Function of Abductor Pollicis Brevis in Hand Movements
The primary function of the abductor pollicis brevis is to abduct the thumb, meaning it moves the thumb away from the palm. This motion is vital for several actions, such as:
- Pinching: The thumb’s ability to move away from the palm allows it to pinch objects between the thumb and fingers. This is an essential motion for tasks like writing, typing, and handling small objects.
- Gripping: The muscle also assists in gripping objects, contributing to the strength of the thumb’s opposition and pinch. This makes it easier to hold onto larger items or manipulate objects in a secure way.
- Hand Dexterity: The muscle’s contribution to thumb movements enhances the overall dexterity of the hand. Fine motor tasks such as buttoning a shirt or picking up a small item rely on the proper function of this muscle.
Overall, without the abductor pollicis brevis, many of the daily tasks we perform with our hands would become significantly more challenging. Its function is integral to both strength and dexterity in the hand.
Clinical Importance of Abductor Pollicis Brevis
The abductor pollicis brevis plays a critical role in many clinical diagnoses and treatments, especially when it comes to conditions affecting hand function. Some of the most common clinical concerns associated with this muscle include:
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
One of the most well-known conditions related to the abductor pollicis brevis is carpal tunnel syndrome. This condition occurs when the median nerve, which innervates the muscle, becomes compressed as it passes through the carpal tunnel in the wrist. As the nerve is compressed, it can lead to symptoms like:
- Numbness
- Tingling
- Weakness in the hand
- Loss of thumb mobility
This compression affects the abductor pollicis brevis and can weaken the muscle’s ability to move the thumb properly, leading to difficulty with common hand movements. Early detection and treatment are crucial to preserving hand function.
Trauma or Injury
Injuries to the hand, such as fractures or dislocations, can also impact the abductor pollicis brevis. If the muscle is damaged, it can impair thumb movement and lead to functional loss. Treatment options may include physical therapy, bracing, or, in severe cases, surgical intervention.
Arthritis and Degenerative Conditions
Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis can also impact the thumb joints and muscles, including the abductor pollicis brevis. Joint inflammation and muscle weakness can make it difficult to perform simple tasks, further highlighting the importance of this muscle in everyday life.
Benefits and Side Effects of Abductor Pollicis Brevis Health
The abductor pollicis brevis contributes significantly to hand health. By maintaining a strong and functional muscle, individuals are able to preserve their hand dexterity and ability to perform a variety of tasks, from typing to carrying objects. However, when this muscle is weakened or affected by conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome, it can severely hinder hand function.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Grip Strength: The abductor pollicis brevis plays a critical role in grip strength, enabling individuals to hold and manipulate objects with precision.
- Increased Hand Dexterity: Thumb movements are crucial for delicate tasks, and a healthy abductor pollicis brevis ensures smooth and effective hand function.
- Improved Overall Hand Function: Proper functioning of this muscle supports overall hand movements, reducing the risk of fatigue and injury during activities that require precision.
Side Effects of Dysfunction:
- Impaired Thumb Movement: If the abductor pollicis brevis is compromised, it can lead to limited thumb mobility, causing difficulty in tasks such as pinching and gripping.
- Hand Weakness: Dysfunction in this muscle can contribute to hand weakness, making everyday tasks more challenging.
- Pain and Discomfort: Conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome can cause pain or numbness in the thumb and hand, impacting quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What causes weakness in the abductor pollicis brevis?
A1: Weakness in the abductor pollicis brevis is often caused by nerve compression (such as in carpal tunnel syndrome), muscle strain, or injury. Chronic conditions like arthritis can also weaken the muscle over time.
Q2: Can physical therapy help strengthen the abductor pollicis brevis?
A2: Yes, physical therapy can help improve strength and mobility in the abductor pollicis brevis. Specific exercises can enhance thumb abduction and reduce discomfort associated with muscle dysfunction.
Q3: How do I know if I have carpal tunnel syndrome affecting the abductor pollicis brevis?
A3: Common signs of carpal tunnel syndrome include numbness, tingling, weakness in the thumb or fingers, and difficulty with tasks like gripping or pinching. A healthcare provider can perform tests to determine the condition.
Q4: Is surgery necessary for treating abductor pollicis brevis dysfunction?
A4: Surgery is typically a last resort if other treatments, such as physical therapy or bracing, fail. In cases of severe nerve compression or injury, surgical intervention may be required.
By understanding the anatomy, function, and clinical significance of the abductor pollicis brevis, we can better appreciate how essential this muscle is to our daily activities. Ensuring its health through proper care and addressing any potential issues promptly can help maintain optimal hand function for years to come.
Customer Reviews
- “I’ve had issues with my thumb and wrist for years, but after learning about the abductor pollicis brevis and carpal tunnel syndrome, I finally understood why it hurt. With therapy, I’ve noticed a big improvement!” — Emma J.
- “Knowing more about this muscle helped me recover after a hand injury. The exercises really made a difference!” — Lucas P.