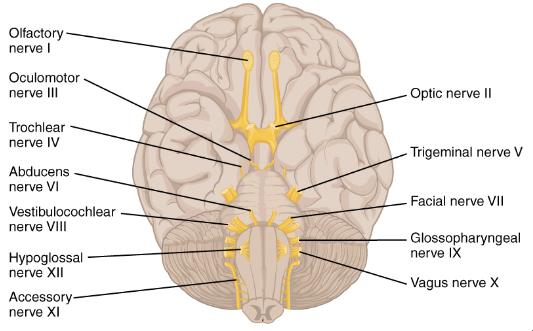
The abducens cranial nerve, also known as cranial nerve VI, plays a crucial role in ocular movement. It primarily controls the lateral rectus muscle, enabling the eye to move outward. Understanding its anatomy and function is essential for diagnosing and treating various neurological disorders.
Anatomy of the Abducens Cranial Nerve
Origin and Pathway
The abducens nerve originates from the abducens nucleus in the pons of the brainstem. It exits the brainstem at the pontomedullary junction and traverses the subarachnoid space before entering the cavernous sinus. Finally, it exits the skull through the superior orbital fissure to reach the lateral rectus muscle.
Structure
The nerve is composed of motor fibers that exclusively control the lateral rectus muscle. It is one of the simplest cranial nerves anatomically, yet its pathway makes it susceptible to injury.
Functions of the Abducens Cranial Nerve
Primary Function
The primary role of the abducens cranial nerve is to innervate the lateral rectus muscle. This muscle is responsible for abducting the eye, meaning it moves the eyeball away from the midline.
Secondary Contributions
While its main task is motor control, the abducens nerve indirectly supports coordinated eye movements through its interactions with other cranial nerves.
Clinical Significance
Disorders Associated with the Abducens Cranial Nerve
- Abducens Nerve Palsy: This condition results in double vision and difficulty moving the affected eye outward.
- Increased Intracranial Pressure: Due to its long pathway, the nerve is vulnerable to pressure changes within the skull.
- Infections or Tumors: Pathologies affecting the brainstem or cavernous sinus can compromise the nerve.
Diagnostic Methods
Physicians use imaging techniques like MRI and CT scans to assess the integrity of the abducens nerve. Additionally, eye movement tests help identify functional impairments.
Benefits and Side Effects
Benefits of a Healthy Abducens Nerve
- Facilitates proper eye alignment and movement.
- Supports visual coordination essential for daily activities.
- Enhances binocular vision, reducing strain and discomfort.
Side Effects of Dysfunction
- Double vision (diplopia).
- Eye misalignment leading to cosmetic concerns.
- Compromised depth perception, affecting tasks like driving or reading.
FAQs About the Abducens Cranial Nerve
Q1: What causes abducens nerve palsy? A: Causes range from head trauma and tumors to diabetes and vascular conditions.
Q2: How is abducens nerve dysfunction treated? A: Treatments include addressing the underlying cause, physical therapy, and in severe cases, surgery.
Q3: Can abducens nerve damage heal naturally? A: Recovery depends on the cause and severity, with some cases improving over time or with targeted therapy.
Q4: Is abducens nerve palsy permanent? A: While some cases resolve, others may lead to lasting impairment without intervention.
Q5: How can I prevent abducens nerve disorders? A: Maintaining good overall health, managing chronic conditions, and protecting the head from trauma are key preventive measures.
Customer Reviews and Expert Opinions
Testimonials
- “Learning about the abducens cranial nerve helped me understand my vision issues better. The detailed explanation was enlightening.” – Sarah T.
- “After my diagnosis, this information gave me clarity and guided my treatment options.” – John M.
Expert Insights
Neurologists emphasize the importance of early diagnosis and targeted interventions for abducens nerve disorders. Regular check-ups and imaging are critical for at-risk populations.
Conclusion
The abducens cranial nerve, despite its simple anatomy, has profound implications for ocular health and vision. Understanding its function, disorders, and treatments empowers individuals to take proactive steps in maintaining their eye health. By addressing dysfunctions promptly, one can avoid complications and ensure optimal vision.